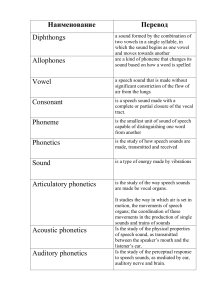
1. Give information about phonetics. Phonetics is the study of speech sounds, their production, and physical properties. It focuses on the physical mechanisms involved in sound production, the articulation of sounds, and how they are perceived by listeners. Phonetics also covers topics like the classification of speech sounds based on their features and categorization into vowels and consonants. It helps in understanding and describing how sounds are produced by the human vocal tract. Additionally, phonetics plays a crucial role in language teaching, speech therapy, forensic linguistics, and other fields where a detailed analysis of speech sounds is necessary. Which branch of the linguistic studies sound and voice. Give examples. Phonetics is the branch of linguistics that studies the physical sounds of human speech, including their production, transmission, and reception. Examples include articulatory phonetics (studying how sounds are produced by the articulators), acoustic phonetics (analyzing the physical properties of sounds), and auditory phonetics (examining how sounds are perceived by the human ear). Phonology, on the other hand, focuses on the abstract, cognitive aspects of sounds within a particular language system, including how sounds function in patterns and structures. 2. What is phonology? Phonology is the study of sounds in language, including the way sounds are organized and used in different languages. It examines the patterns of sounds, their roles in forming words, and how they are pronounced and perceived by speakers. In addition to studying the sounds themselves, phonology also looks at how sounds interact with each other within a language system. This includes understanding speech sounds, their distribution, and the rules governing their use in different linguistic contexts. 7. Give information about articulatory phonetics. Articulatory phonetics is a branch of phonetics that studies how speech sounds are produced using the articulators in the vocal tract, such as the tongue, lips, and palate. It focuses on the physical processes involved in creating sounds and how they are classified based on articulatory features like place and manner of articulation. Understanding articulatory phonetics helps linguists analyze and describe the production of speech sounds in different languages. 3. What is the difference between phonetics and phonology? Phonetics deals with the physical sounds of speech, focusing on their production, transmission, and reception. It analyzes the properties of individual speech sounds, including their articulation and acoustic characteristics. Phonology, on the other hand, examines how sounds function in a particular language system. It studies the patterns and rules governing how sounds are organized and used to convey meaning in a language. While phonetics is concerned with the actual sounds themselves, phonology is more concerned with the abstract, underlying linguistic structures that govern the sounds within a language. 4. What is phoneme? A phoneme is the smallest unit of sound that distinguishes words in a language. It represents the sounds that can change the meaning of a word when substituted. For example, in English, changing the initial phoneme in "cat" from /k/ to /p/ results in a new word, "pat." Phonemes are essential in language as they help differentiate words and convey meaning through their distinctive sound patterns. Understanding phonemes is crucial in fields like linguistics, psychology, and language development. 5. What is the difference between language and speech. Language refers to a system of communication using symbols and rules to convey meaning, encompassing grammar, syntax, and vocabulary. Speech, on the other hand, specifically refers to the vocalized form of language produced by the human vocal apparatus. Language encompasses various forms of communication, including writing and signing, while speech specifically involves the production and articulation of sounds. In essence, language is the broader system of communication, while speech is a specific modality within that system. 6. 8. Give information about acoustic phonetics. Acoustic phonetics is a subfield of phonetics concerned with the physical properties of sounds in speech. It focuses on how sounds are produced, transmitted, and perceived. Acoustic phoneticians use technology to analyze sound waves and frequencies to understand speech sounds. By studying acoustic characteristics like pitch, intensity, and duration, researchers can gain insight into speech patterns, accents, and variations across languages. Acoustic phonetics plays a crucial role in fields like linguistics, speech therapy, and language technology. 9. Give information about auditory phonetics. Auditory phonetics is the branch of phonetics that focuses on how speech sounds are perceived by the human auditory system. It studies how sounds are processed, recognized, and interpreted by the brain. Researchers in this field examine aspects such as pitch, timbre, loudness, and duration to understand how different sounds are perceived and distinguished in speech. By studying auditory phonetics, researchers aim to gain insight into how humans process and understand spoken language. 10. What does morphology study? Morphology is the study of the forms and structures of words in language. It examines how words are formed, their internal structure, their meanings, and how they are related to other words within a language. Morphology also deals with the ways in which words can be modified to create new words through processes like affixation (adding prefixes or suffixes), compounding (joining two words together), and more. In essence, morphology focuses on the smallest units of meaning in language and how they combine to create words.