Косвенная речь
реклама

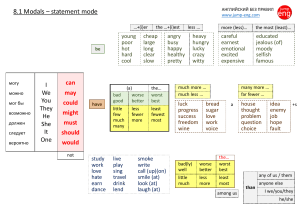
Косвенная речь Say Tell Advise Explain promise Say – не следует местоимение, существительное, обозначающее лицо, к кому обращена речь. Tell следует местоимение, сущ., обозначающее лицо, к кому обращена речь. He said (that) he was going to Italy. He told Brian (that) he was going to Italy. Если глагол главного предложения стоит в прошедшем времени, то времена глаголов в придаточном предложении также употребляются в прошедшем времени. При переходе прямой речи в косвенную не изменяются глаголы: must, would, could, might, should, ought to. “He might visit us”, mum said. Mum said that he might visit us. General questions: Molly asked, “Are you leaving at midnight?” Molly asked if I was leaving at midnight. Special questions: John asked, “What did he tell you about his trip?” John asked what he had told me about his trip. “Do you know where I’ve put my hat?” he said to her. “Would you like me to drive you into town?” she asked me. “Why did you say that to me?” she asked me. “What have you bought me for Christmas?” the little boy said to his parents. What’s your name? Did you see the robbers? What were they wearing? How do you think they got in? What did they take? Has this ever happened before? Reporting verbs: order, ask, advise, offer, warn, beg, suggest. ask + to-Infinitive ask + not to-Infinitive Example: “Can you help me Tom?” Ann asked Tom to help her. Miss Prim told her students not to talk when she’s talking. She told them to give their homework to her at the end of each lesson. She asked them not to write on the desks. Then she told them to put their hands up if they had a question. She also asked them not to eat in the classroom. She told them to write everything in pen and asked them to throw their rubbish into the wastepaper bin. Finally she told them not to leave the classroom without permission.