Практичекая грамматика английского языка(презентация)
реклама

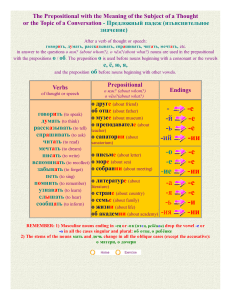
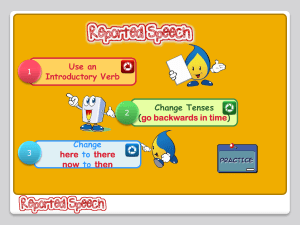
Практическая грамматика английского языка Специальность: современные иностранные языки (1 курс ) Цель данного курса – объяснить ключевые морфологические и синтаксические особенности грамматического строя современного английского языка, обеспечить правильность их понимания и научить студентов правильно применять грамматические правила при переводе, а также в устной и письменной английской речи. Важнейшими задачами курса являются : - формирование, развитие и совершенствование грамматических навыков распознания, понимания грамматических форм и конструкций в опоре на формальные признаки членов предложения и частей речи; - формирование и совершенствование навыков употребления грамматических форм и конструкций в составе предложения/фразы различных структурных типов, а именно: - овладение конструкциями, выражающими субъектнопредикатные отношения; - грамматическими категориями, выражающими действие и характер его протекания; - средствами выражения определенности-неопределенности, единичности-множественности предметов и явлений; качества предметов, явлений; интенсивности качества; порядка и количества предметов. The Noun • Semantic characteristics: proper, common( concrete, abstract, material), collective(group, multitude, mass) • Composition: simple, derived, compound • Gender: masculine nouns, feminine nouns, neuter nouns, feminine suffixes, political correctness • Case: use(personal names, personal nouns, collective nouns, higher animals, geographical names, newspapers and institutional names, temporal or distance nouns, nouns of special interest to human activity, set expressions), types of the genitive • Number: regular plurals, irregular plurals, singular invariables, plural invariables The Article • Articles with variable concrete nouns: the indefinite article (classifying, generic, numerical f-ns), the definite article (specifying (the situation, the context, the meaning of the noun, limiting attributes) and generic f-ns)) • Articles with abstract nouns • Articles with material nouns • Articles with proper nouns : personal names, geographical names, calendar items, miscellaneous names • Articles in some syntactic relations : the subject, an object, an adverbial modifier, an attribute, a predicative, an apposition • Articles with some semantic groups of nouns : seasons, parts of the day, meals, parts of the body, specific periods, media and communications… • Leaving out articles: notes, notices, instructions, signs, labels, double expressions, introductory phrases… The Adjective • Semantic Characteristics: qualitative (descriptive and limiting), relative • Composition: simple, derived, compound • Degrees of Comparison: gradable and non-gradable • Functions of Adjectives: an attribute, a predicative, a part of a compound verbal predicate, an objective predicative, a subjective predicative, an adverbial modifier) • Order of Adjectives The Numeral • • • • Cardinal: indicate number Ordinal: indicate order Dates and Fractions: common, decimal Functions: functions of nouns and adjectives The Adverb • Classification: of time, of frequency, of place and direction, of manner, of degree, focusing adv., viewpoint adv., attitudinal adv., conjunctive adverbs • Forms: formed from other words, not formed from other words, fixed phrases • Degrees of Comparison: mostly adverbs of manner • Syntactic Functions: modify single words, phrases, sentences • Place of Adverbs: front, mid and final • Adjectives and Adverbs Compared: coincidence in form, difference in meaning The Pronoun • • • • • • • • Personal: singular, plural, structural meanings Possessive: singular, plural, possessives or the definite article Reflexive: singular, plural, reflexive and emphatic pronouns Demonstrative: singular, plural, that or it, set expressions with demonstratives Indefinite: indefinite pronouns proper, distributive and quantitative pronouns, compounds Interrogative: variable and invariable, persons and things Reciprocal: two persons, more than two persons Conjunctive: the choice of a pronoun depending on the type of the subordinate clause, persons and things The Present Simple Tense • Formation • Meaning and Use • recurrent actions • general truth and facts, permanent characteristics • series of actions • more immediacy or dramatic effect in a past narrative(instead of the Past Simple) • a single action at the moment of speaking • future actions • exclamatory sentences The Present Continuous Tense • Formation • Meaning and Use • an action in progress at the moment of speaking or at present period • emotional coloring of someone’s typical actions or traits (always, constantly) • emotional coloring • future actions The Present Perfect Tense • • • • • • Formation Meaning and Use states started in the past and are still continuing in the present an action happened in the past and may happen in the future an accomplished action with relevance to the present news broadcasts and reports to start a story, before moving into past tenses • in time clauses for future • with superlatives The Present Perfect Continuous Tense • Formation • Meaning and Use • an ongoing action or state began in the past and is still going on or has just finished • -to focus on the duration • -a temporary state or action(may change) • -to explain a present result • -emotional coloring Simple or Continuous • • • • Perfect Simple Perfect Continuous completion repeated actions permanent situation focus on present result • • • • continuation duration of action temporary situation focus on activity The Past Simple Tense • • • • • • • • Formation Meaning and Use a single completed action in the past -an action which occupied a whole period of time and now is over -sequences of actions -repeated actions or actions which took place at the same time -states or actions at a given past moment -future actions viewed from the past Present Perfect or Past Simple Present Perfect • • • • unfinished action/state unfinished time present relevance indefinite time Past Simple • • • • finished action/state finished time no present relevance definite time The Past Continuous Tense • • • • • Formation Meaning and Use an action going on at a given moment in the past -an action going on at a given period in the past -emotional coloring, someone’s typical traits(always, constantly) • -future actions viewed from the past • Clauses of time with as and while: Past Continuous or Past Simple The Past Perfect Tense • Formation • Meaning and Use • an action completed before a given past moment and viewed back from that past moment(a single point action, an action of some duration and a recurrent action) • -an action which began before a given past moment and continued into it or up to it • -clauses of time(when, before, after, as soon as, till/until, scarcely…when, hardly…when…) • -to express unfulfilled past intentions(hope, expect, want, plan, wish…) The Past Perfect Continuous Tense • Formation • Meaning and Use • an action which began before a given past moment and continued into it or up to it • an action which was in progress just before a given past moment and it somehow affects the past situation(usually no time indications) • Note: full negation – Past Perfect Simple instead of Past Perfect Continuous Future Tenses • • • • • • • • • • • • Prediction guesswork, analysis, judgment – Future Simple evidence in the present – to be going to + infinitive a (temporary) action in progress at a given moment in the future – Future Continuous an action we predict to be completed by a particular time in the future – Future Perfect(soon, by then) Decisions and Intentions a decision at a time of speaking – Future Simple an intention which has already been decided on – to be going to Arrangements an event( action) in the future which has already been arranged by the time of speaking – Present Continuous -an action(event) is a part(result) of an arrangement made in the past – Future Continuous Other Future Meanings(timetables, routine events, smth inevitable, statements of fact…) The Passive Voice Formation to be + past participle generally only transitive verbs can be made passive tenses used in the passive(8 tenses) Use: reasons to use the Passive Types of the Passive Constructions: the Direct Passive, the Indirect Passive, the Prepositional Passive Passive Patterns: passives with get, passive – ing forms, passive infinitives, have/get + object + past participle The Sequence of Tenses • Definition: absolute and relative use of tense forms • Meaning and Use : the relative use of tenses is mainly observed in subordinate object clauses and sometimes in the clauses of purpose, subjective and objective clauses • Future- in- the- Past: the Future Simple-in-the-Past, the Future Continuous-in-the-Past, the Future Perfect-in-the-Past, the Past Continuous, to be to + infinitive, to be going to + infinitive, the Past Simple Reported Speech • Time and Place Changes. Sequence of Tenses in Reported Speech • report verbs • -change of tenses, pronouns, adverbs • -cases when we do not change tenses • -questions, commands, requests… Вопросы к зачету Основная литература 1. Крылова И. П. Сборник упражнений по грамматике английского языка: Уч. Пособие для ин-тов и фак. ин. яз. – 9-е изд.- М: КДУ, 2004. – 432с. 2. Крылова И.П. , Гордон Е. М. Грамматика современного английского языка: Учебник для ин-тов и фак. ин. яз.- 8-е изд. – М. : КДУ,2002 3. Morphology. A Selection of English Grammar Exercises; сост. В. О. Французова. – 3-е изд. доп. и перераб.- Мн.: «Лексис», 2005 4. Prodromou L. Grammar and Vocabulary for First Certificate. – Longman, 2000 5. Thomson A.J., Martinet A. V. A Practical English Grammar. – 3rd ed. – Oxford: «Oxford University Press», 1999 Выполнила:преп. Л.Н. Пышняк