Видовременные формы английского языка Файл
реклама

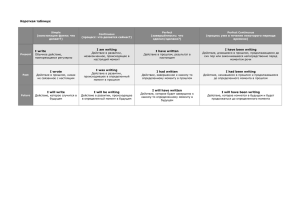
Практикум для самостоятельного повторения видовременных форм глаголов английского языка Данное пособие может быть использовано в старших классах средней школы и на курсах при среднем и высшем учебных заведениях. В методической разработке рассматриваются правила образования и употребления форм глаголов в активном залоге, во второй части даны тесты на проверку усвоения темы, как средство самоконтроля уровня знаний при самостоятельной подготовке к зачетам или экзаменам. Содержание Введение Образование и употребление видовременных форм глагола Тесты для самостоятельной работы Ключи к заданиям Введение Учебное пособие предназначено, прежде всего, тем, кто готовится к экзаменам самостоятельно. Оно может быть использовано в старших классах средней школы и на курсах при среднем и высшем учебных заведениях. Цель пособия — помочь учащимся и студентам повторить из школьного курса видовременные формы глагола. Пособие состоит из двух разделов: 1. Теоретическая часть; 2. Практическая часть. В теоретической части рассматриваются правила образования и употребления форм глаголов в активном залоге. Наиболее развернуто дается объяснение употребления форм, так как в английском языке в изъявительном наклонении глагол образует 16 (12 + 4 будущего в прошедшем) видовременных форм в зависимости от времени осуществления и типа действия. В практической части вы найдете тесты на проверку усвоения темы. Данный раздел может быть использован как средство самоконтроля уровня знаний при самостоятельной подготовке к зачетам или экзаменам. Приступая к работе с тестами, необходимо вначале изучить грамматический материал с помощью предыдущего раздела. Каждый из тестов в целом представляет собой задание повышенной сложности, и их успешное выполнение свидетельствует о надлежащем усвоении темы. При работе с тестами могут понадобиться словарь и грамматический справочник. В конце сборника к каждому тесту даются ключи, которые помогут вам проверить правильность ваших ответов. 1. Образование и употребление видовременных форм глагола Взаимосвязь времени и характеристики действия Время Характеристика действия Настоящее - Present Неопределенное - Simple (Indefinite) Длящееся - Continuous (Progressive) Прошедшее - Past Совершенное - Perfect Будущее - Future Совершаемое в течение периода времени - Perfect Continuous (Progressive) Основные значения: 1. Неопределенные времена: - обычные повседневные действия 2. Длящиеся: - действие в развитии, в процессе; - эмоциональная окраска; 3. Совершенные: - действие, совершенное к какому-то или до какого-то момента (значит, всегда должен подразумеваться этот момент). 4. Совершаемые в течение периода времени: - всегда должен быть указан период, без указанного периода эта форма не употребляется. Таблица видовременных форм глагола Simple Continuous Perfect Past I read a book yesterday.Вчера я прочитал книгу. I was reading a book when my mother came.- Я читал книгу, когда пришла мама I had read a book to 04:00 p.m.- Я закончил читать книгу к 4:00 часам. Future I shall read a I shall be read- I shall have I shall have been book tomor- ing a book to- read a book by reading a book row.- Я morrow at this 05:00 p.m.- К 5 for an hour when прочту книгу moment.часам я прочту she comes.- Я завтра. Завтра в это книгу (закончу буду читать уже время я буду читать). час, когда она читать книгу. придет. Present Perfect Continuous I read a I am reading a I have read a I have been readbook.- Я book.- Я читаю book.- Я ing a book for an читаю книгу. книгу. ( в только что hour.- Я читаю (обычное данный прочел книгу книгу в течение действие) момент) (совершенное 1 часа. (действие к моменту в течение речи) определенного времени) Обычное действие, обычный факт Процесс действия I have been reading a book for an hour when she came.- Я читал книгу уже час, когда она пришла. Законченное Действие в действие течение определенного времени Формы настоящего времени — The Present Indefinite Tense Образуется: инфинитив без «to», в 3-м лице единственного числа прибавляется окончание - s/es. Вопросительная и отрицательная форма — с помощью вспомогательного глагола do/does. He walks the dog every night. Does he go to school? He doesn’t love jazz. Употребляется для обозначения действий следующего характера: 1. Обычное, регулярное, привычное, повторяющееся действие. Часто сопровождается соответствующими обстоятельствами времени - often, every day, usually, rarely/seldom, always. They love children. He goes to school every day. We usually stay here for summer. 2. Прописная истина, всем известный факт. Leaves fall down in autumn. The sun sets in the west. 3. Вместо Present Continuous с глаголами физического восприятия, умственной активности, эмоционального состояния to hear, to see, to feel, to understand, to know, to love, etc., которые не употребляются в форме Continuous (потому что по своей сути обозначают процесс или состояние, а не действие как таковое). I am listening to you but I cannot hear you properly. Now I understand what you mean. 4. Вместо Future Indefinite в придаточных времени и условия после союзов if, when, as soon as, after, before, while, etc. He will go there when/if it stops raining. They will tell us as soon as they find out what’s happened. 5. Вместо Future Indefinite с глаголами движения to leave, to go, to arrive, etc. для обозначения будущего запланированного действия, часто действия по расписанию в ближайшем будущем. The train leaves at 7 pm. We arrive this Sunday. Формы настоящего времени — The Present Continuous Tense Образуется: глагол «to be» в форме Present Indefinite + Present Participle/Participle I. Образование Present Continuous Tense am doing smth is are Употребляется для обозначения следующих действий: 1. Действие в развитии в настоящий момент времени/в момент речи за исключением глаголов физического восприятия, умственной активности, эмоционального состояния to hear, to see, to feel, to understand, to know, to love, etc., которые не употребляются в форме Continuous. Now I know what you are talking about. Look, the dog is running away! I can’t hear what you are saying. 2. Действие временного характера, протекающее в настоящий период времени. He works at the hospital but he is writing his thesis now. She gets up at 7 every morning but today she is getting up at 8 am. 3. Эмоциональная окраска (характерна для разговорной речи, может заменять форму Present Indefinite, отражая тем самым эмоциональное отношение говорящего к происходящему). She is always grumbling! (Вечно она ворчит!) Whenever I see her, she is always reading! (Когда бы я ее ни увидела, она все время читает!) 4. Действие в ближайшем будущем, часто с глаголами движения. I am leaving on Sunday. They are arriving tomorrow. I am doing this next week. Формы настоящего времени — The Present Perfect Tense Образуется: глагол «have» в форме Present Indefinite + Past Participle/Participle II Образование Present Perfect Tense have/has done smth Употребляется в разговорной речи или при передаче прямой речи. ThePresentPerfect Обозначает: Действие, совершенное к моменту речи: время совершения действия не имеет значения, главное, что в момент речи налицо результат этого действия. (Я написал сочинение — когда, вчера, неделю назад — неважно. Важно, что вот она, тетрадка, в которой есть это сочинение. Я был в Ленинграде три раза — неважно, когда, важно, что там был). Главное в этом времени, что оно НАСТОЯЩЕЕ, то есть если есть малейший намек на то, что действие совершено в прошлом, эту временную форму употреблять нельзя. Почувствуйте разницу!!! I have lost my ticket. (= Теперь надо покупать билеты) I lost my ticket in the morning/in the tram. (=Утро закончилось/в трамвае, когда я утром ехала на работу) Выбор времени зависит только от тебя, поэтому если ты ощущаешь какое-то действие, как прошедшее, употребляешь форму прошедшего времени; если ты ощущаешь действие, результат которого имеется в данный момент, и это единственное, что для тебя важно, значит, употребляешь Perfect. He has gone out. (=Ушел и еще не вернулся) He went out. (Выходил, но уже вернулся назад) I have seen a wolf in this forest. (= Как-то раз; говорится, чтобы знали, что здесь водятся волки) I saw a wolf in the forest. (Сегодня утром, когда проезжал мимо леса на машине) Mr.P has written three books. (Раз еще жив, глядишь, еще напишет) Pushkin wrote 10 poems. (Уже помер и больше не напишет) NB: никогда не употребляется после WHEN. Формы настоящего времени — The Present Perfect Continuous Tense Образуется: глагол «be» в форме Present Perfect + Present Participle/Participle I Образование Present Perfect Continuous Tense have/has been doing smth Употребляется в разговорной речи или при передаче прямой речи. Значение: 1. Всегда подразумевает период. Отличается от Perfect так же, как неопределенные от длящихся: ты намеренно выделяешь процесс, что, как правило, одновременно придает эмоциональную окраску, именно поэтому эта форма характерна для разговорной речи. I have been doing this for 3 hours, and now you are telling me you don’t need it?! (момент речи исключен) I have been calling her since early morning/since I arrived. (момент речи включен) (точка отсчета обозначается прошедшим действием) Why are you breathing so hard? I have been running. (момент речи исключен, период не указан, но подразумевается) Формы прошедшего времени — The Past Indefinite Tense Образуется: II-я форма неправильных глаголов или + ed к инфинитиву правильных глаголов. He walked the dog every night. Did he go to school? He didn’t love jazz. Употребляется для обозначения действий следующего характера: 1. Законченное действие в прошлом (однократное или постоянное). He finished the letter yesterday. They lived on a farm. I read the book from 3 to 5. (Действие началось и закончилось) Для передачи часто повторяющегося действия в прошлом употребляются также used to - «одно время делали, но затем перестали» и would - «делали и делали» We used to go there every Sunday when we lived there. We would go there every Sunday for fun. 2. Ряд последовательных действий в прошлом. I came home, switched on TV, made my coffe and sat down to watch TV. 3. Вместо формы Continuous с глаголами, которые в этой форме не употребляются. I did not hear when you were saying this. 4. Вместо Present Indefinite в придаточных изъяснительных при переводе прямой речи в косвенную по согласованию времен. He said he went there every day. 5. Вместо будущего в прошедшем в придаточных времени и условия в косвенной речи. He said he would do it, when/if he arrived. Формы прошедшего времени — The Past Continuous Tense Образуется: глагол «to be» в форме Past Indefinite + Present Participle/Participle I Образование Past Continuous Tense was/were doing smth Употребляется для обозначения следующих действий: 1. Действие в развитии в какой-то момент в прошлом, который может быть выражен лексически или зафиксирован соответствующим придаточным времени. Исключение составляют глаголы физического восприятия, умственной активности, эмоционального состояния to hear, to see, to feel, to understand, to know, to love, etc., которые не употребляются в форме Continuous. I was doing my homework at 3 pm yesterday. I was watching TV when you called. I opened the door and looked out. The car was standing where I had left it. NB: для этой формы необходим именно момент - В, поэтому если речь идет об отрезке времени в прошлом, т.е. с 3 до 5, с понедельника по пятницу, 2 года, надо употреблять Past Indefinite, хотя в русском языке в этом случае употребляется форма глагола несовершенного вида (что делал?), которая в сознании русскоговорящих ассоциируется с формой длящихся времен в английском, отсюда, по велению сердца, часто возникают ошибки. В этом случае лучше руководствоваться головой. 2. Фоновое описательное действие при описании ситуации в прошлом. It happened last winter. The snow was falling hard, a strong wind was blowing. I had to go out with Jan that night. 3. Эмоциональная окраска (характерна для разговорной речи, может заменять форму Past Indefinite, отражая тем самым эмоциональное отношение говорящего к происходящему). Whenever I met her, she was always reading! Когда бы я ее ни увидела, она все время читает! I was writing this letter from 3 to 5 yesterday! (Отражает либо твое крайнее возмущение непосильным трудом, либо справедливое восхищение собственным трудолюбием. Если никаких эмоций ты в это предложение не вкладываешь, значит, просто Past Indefinite). 4. В косвенной речи по согласованию времен будущее действие в контексте прошедшего времени, часто с глаголами движения. He said he was leaving the following Sunday. They mentioned that they were arriving the next day. She asked me what I was wearing to the party. 5. Вместо Future Continuos-in-the-Past в придаточных времени/условия. Формы прошедшего времени — The Past Perfect Tense Образуется: глагол «have» в форме Past Indefinite + Past Participle/Participle II Образование Past Perfect Tense had done Никогда не употребляется ни самостоятельно, ни в контексте настоящего времени, потому что является так называемой «относительной» видовременной формой, которая указывает только на то, что какое-то действие было совершено до какого-то другого действия в прошлом или к какомуто моменту времени в прошлом, т.е. указывает на последовательность совершения действий в прошлом, а не на время совершения действия. Отсюда вытекают следующие особенности употребления этой формы: 1. Поскольку эта форма обозначает ПРЕДПРОШЕДШЕЕ действие, соответственно, для ее употребления необходимо иметь ПРОШЕДШЕЕ действие. When she came, he had already calmed down. I finished typing at seven. The post had already gone. 2. Эта форма НЕ может употребляться, если есть точное указание времени в прошлом. Она употребляется только в значении »by» - к какому-то моменту в прошлом. Before the war she worked as a reporter. By midnight she had already changed her mind. 3. В придаточных времени с союзами, которые указывают на последовательность совершения действия (before, after), Past Perfect усиливает это значение, поэтому если не имеется в виду, что одно действие произошло ТОЛЬКО до/после того, как было совершено другое, употребляется Past Indefinite. He had finished it by 3 pm yesterday. He did it after I had asked him. Only when I had seen it myself, I realized how interesting it was 4. Русские выражения «только он/не успел он» переводятся при помощи следующих конструкций, часто с инверсией (обратным порядком слов, когда часть сказуемого стоит перед подлежащим, что в принципе недопустимо в английском языке) для придания эмоциональной окраски. He had hardly done smth … when smb did smth Hardly had he done smth … when smb did smth No sooner had he done smth … than smb did smth Hardly had he entered the room when the telephone rang. No sooner had he said this, when he realized the mistake he had just made. 5. Вместо Past Indefinite в косвенной речи в придаточных изъяснительных по согласованию времен. He told me he had heard that before. He said he had met her two years before. NB: Согласование времен не соблюдается, если в косвенную речь переводится предложение, содержащее точное указание времени в прошлом или сложное предложение с придаточным времени. He said he worked there in 1940. He said he ran out when he heard the fire alarm. 6. Вместо формы Perfect Continuous с глаголами, не употребляющимися в длительной форме (см. Continuous). I had known her for years. 7. Вместо будущего Perfect в прошедшем в придаточных времени и условия (см. Indefinite). He said he would do that as soon as/if he had received written instructions. Формы прошедшего времени — The Past Perfect Continuous Tense Образуется: глагол «be» в форме Past Perfect + Present Participle/Participle I Образование Past Perfect Continuous Tense had been doing smth Значение: 1. действие, которое началось и развивалось в течение периода времени до какого-то момента в прошлом, включая или исключая этот момент. Her eyes were red. She had been crying again. We had been discussing this for two hours when the storm broke out. (окончание периода обозначается прошедшим действием) By the time we got home we had been walking for 3 hours. 2. вместо Present Perfect Continuous в косвенной речи по согласованию времен He said he had been doing that for two weeks. Формы будущего времени — The Future Indefinite Tense Образование Future Indefinite Tense shall/will do smth Обозначает: будущее действие. He will go to the cinema tomorrow. Формы будущего времени — The Future Continuous Tense Образование Future Continuous Tense shall/will be doing smth Обозначает: 1. Действие в развитии в какой-то момент в будущем. He will be calling you tomorrow at 5. 2. Намерение сделать что-либо. I will be staying with them next week. Формы будущего времени — The Future Perfect Tense Образование Future Perfect Tense shall/will have done smth Обозначает: Действие, которое будет совершено к какому-то моменту в будущем. He will have done it by the time you come home Формы будущего времени — The Future Perfect Continuous Tense Образование Future Perfect Continuous Tense shall/will have been doing smth Обозначает: Действие, которое будет развиваться в течение некоторого периода времени в будущем. Указание периода ОБЯЗАТЕЛЬНО. He will have been doing this for 3 hours when you arrive. Все те же значения для будущего в прошедшем, только вспомогательный глагол меняется на would. 1. 2. Тесты для самостоятельной работы 2.1. Примеры выполнения заданий: Разберем ряд упражнений по теме. Прочитайте следующие примеры и их перевод на русский язык: 1. I go to school. 1. Я хожу в школу (каждый день). 2. I am going to school. 2. Я иду в школу (сейчас). 1. I have come to school. 4. I have been going to school for 20 min. 3. Я пришел в школу (только что). 4. Я иду в школу уже 20 минут. Задание1. Вставьте to write в нужную форму: 1. As a rule, he … tests well. 2. What … you … tomorrow at 10? 3. Yesterday they … … … tests from 10 till 12 o’clock. 4. Who … … this letter? 5. I … some letters last week. 6. What … she … in the evening yesterday? 7. I … not … this letters now. I … … it in some days. 8. I … … an article, you may take it. Ответы на задание 1. 1. Writes- В этом предложении речь идет о привычном действии, это подтверждается словами asarule- как правило. 2. Will … bedoing- На данном примере глагол поставим в будущее простое время Future Indefinite, так как здесь время определяется отрезком времени tomorrow. 3. Hadbeenwriting- В этом случае известно время, за которое происходило действие в прошлом, поэтому глагол поставим в Past Perfect Continuous, 4. Haswritten- Действие произошло в недавнем прошлом, письмо написано и лежит передо мной, следовательно глагол стоит в Present Perfect. 5.Wrote- Так как действие совершено на прошлой неделе, глагол поставим в Past Indefinite. 6. Was …writing- Действие происходит в какой-то момент в прошлом и глагол стоит в Past Continuous. 7.Am … writing; shall …write- В первом предложении действие происходит в момент речи (now-сейчас), поэтому глагол поставили в Present Continuous. Второе действие планируется через несколько дней (in some days- через несколько дней). Следовательно, глагол поставим в Future Indefinite. 8. Havewritten- Действие совершено только что: я написала статью, ты можешь взять ее. Следовательно, глагол поставим в Present Perfect. 2.2. Задания для самостоятельной работы: Задание1. Поставьте глаголы в нужную форму: 1. We often (write) letters to our parents. 2. What you (do) now? 3. He just (go) away. 4. She (not see) him for three years. 5. They (go) to Moscow next week? 6. I already (tell) you the answer yesterday. 7. At present she (not work) at school. 8. You (switch off) the light before you left the house? 9. When I came to her, she (write) a letter. 10. He (not like) loud music. Задание 2. Замените форму глагола с Present Simple на Present Continuous: 1.He looks through the papers every day. 2. They play volleyball very well. 3. He listens to the latest news in the morning and in the evening. 4. We watch TV together. 5. She works at school. 6. Your children usually ask many questions. 7. My sister translates this book every night. 8. They do their home task very well. Задание 3. Поставьте глаголы в скобках в одно из прошедших времен: 1.When I (come) the lecture already (start). 2. They (go) to Moscow some days ago. 3. When I came he (leave), so we only had time for a few words. 4. He suddenly (understand) that he (travel) in the wrong direction. 5. Our teacher (speak) many foreign languages. 6. Where (be) Bob? He (play) tennis. 7. I (go) home when we met. 8. My son (play) the piano. 9. We (discuss) your plan yesterday at 10 o’clock. 10. It (rain when I went for a walk. Задание 4. Заполните пропуски подходящей формой: А) do B) does 1. I … not like playing chess. 2. Where … she live? 3. We usually … our homework at time. 4. He … his task tomorrow. 5. What time … you get up? C) will do 6. They … not want to go shopping on Saturdays. Задание 5. Тесты «Present Tenses» К каждому вопросу даны несколько вариантов ответа. Выберите тот, который считаете правильным. Начало формы 1. I have found a good job. It’s in Brazil. I … to go to Brazil. I don’t like living in cold climates. have always wanted always wanted want is wanting 2. Zeta has sent me two letters; neither of which ….. . has arrived have arrived arrive is arriving 3. Willy ….. from his Uncle Alex since the latter immigrated to Canada. does not hear have not heard has not heard is not hearing 4. About 85 percent of American students ….. public schools, which are supported by state and local taxes. attend are attending have attended have been attending 5. Be careful with paint. It ….. a certain amount of lead. contains is containing has contained contained 6. Look here! I simply refuse to believe what you ….. me now. are telling have been telling have told tell 7. My cousin Jake has got a lot of books, most of which he ….. . doesn’t read hasn’t been reading hasn’t read isn’t reading 8. Carol and I are old friends. I ….. her since we studied in high school together. know have known are knowing have been knowing 9. The government is worried because the number of people without jobs ….. . increases has increased is increasing has been increasing 10. David is quite an athlete. He wants to be strong and healthy that’s why he ….. every morning. is jogging has jogged jogs has been jogging 11. Her family ….. from town to town ever since she can remember. is moving has moved moves has been moving 12. Jeremy ….. basketball this season; he wants to concentrate on his studies. doesn’t play hasn’t been playing isn’t playing hasn’t played 13. I have just applied for a job in the local hospital, now I ….. for an answer from them. wait have been waiting have waited am waiting 14. Nora, you look awfully tired. What ….. all day? do you do are you doing have you been doing have you done 15. I ….. Mario for some time since he left Milan a few years ago. haven’t seen don’t see didn’t see Тест по теме «Past Tenses» Начало формы 1. It wasn’t raining when I looked out of the window; the sun was shining. But it ….. earlier. That’s why the ground was wet. rained was raining had rained had been raining 2. Scarcely ….. out of the window when I saw a flash of light. had I looked I was looking had I been looking was I looking 3. The Browns ….. in a large house when their children were at home, but they moved to a small three-room apartment after the children grew up and left home. lived had lived used to live were living 4. Everybody was laughing merrily while Harris ….. them a funny story. told had told was telling had been telling 5. A strong wind ….. and I decided to put on a warm coat. blew had blown was blowing had been blowing 6. Yesterday I came up to a stranger who looked like Jane Faster and started talking to her. But she wasn’t Jane. It was clear I ….. a mistake. made was making had made had been making 7. I saw Paul at the airport. He ….. for his brother’s plane to arrive from Canada. had been waiting was waiting waited had waited 8. He was taken to the police station because he ….. into a car in front of him. crashed had crashed didn’t crash wasn’t crashing 9. Before I went to bed I decided to check the front door. I was sure my sister ….. it. And I was right! didn’t lock hadn’t locked locked had locked 10. Our clothes were wet because we ….. in the rain. had been walking had walked were walking walked 11. I found the way to her house quite easily because Nora ….. it to me very well. had been describing had described was describing described 12. We ….. TV for ten minutes when the electricity went off. watched were watching had watched had been watching 13. Our neighbours called the police when they found out that somebody ….. into their house. broke was breaking had broken had been breaking 14. The two boys came into the house. One had a black eye and the other a cut lip. They ….. . had been fighting had fought fought were fighting 15. In 1912 the Titanic ….. an iceberg on its first trip across the Atlantic, and it sank four hours later. had hit hit was hitting had been hitting Тест по теме «Future Tenses» Начало формы 1. It is going to rain, and I am not sure if I will have painted the roof before it ….. raining. starts will start will be starting will have started 2. I don’t know if he ….. to join us, but if he does, it will change my plans. will make up his mind will have made up his mind makes up his mind has made up his mind 3. Ask Tom if he ….. in the chess tournament next week. will take part takes part will be taking part will have taken part 4. You can’t see this film on TV tonight, they ….. it only next Sunday. are showing will show show will be showing 5. The windows in my flat are dirty. I haven’t cleaned them yet. I ….. it this Saturday. will do will be doing am doing am going to do 6. Susan ….. the house before her husband comes home. won’t leave won’t have been leaving won’t have left won’t be leaving 7. Do you think you ….. here in a few years’ time? will you still be working you will still be working you are still working will you still work 8. She is not sure if she ….. his telephone number in the telephone directory. will find will have found finds will be finding 9. I ….. to London tomorrow; I will phone you when I arrive. will come am coming will be coming will have come 10. By the first of December this year I ….. here for fifteen years already. will have been working will work will have worked will be working 11. I will be back soon. I hope you ….. your translation by the time I come. will have finished will finish will be finishing will have been finishing 12. Lionel will come to London as soon as you ….. a place for him to stay. have found will find will have found are going to find 13. I don’t know when Professor Johnson ….. to his office, but when he comes, I’ll speak to him about it. comes will come will have come is coming 14. If I ….. George tomorrow, I will tell him to come and see you. meet will meet am going to meet will be meeting 15. I’ll come home late tomorrow. I ….. out with my friend. will be dining will dine will have been dining am dining Тест по теме «Sequence of Tenses» Начало формы 1. Seeing that I was nervous, Sue advised me ….. for the answer till the following day. must wait to wait would wait 2. She asked me about my schedule for the next week and I answered that I ….. it yet. hadn’t known didn’t know wouldn’t know 3. Nina said Lucy complained that her friends never ….. any attention to what she told them. would pay paid had paid 4. Alice told me ….. that coat because it wasn’t long enough. bought to buy not to buy 5. They explained to us that the Local History museum, which was usually open every Sunday, ….. that day. was closed was being closed had been closed 6. David told his friend that ….. his bicycle whenever he liked. might he use he might use he had used 7. Tom said that he had been late for work that morning, and he added that he ….. before. had never been late was never late never had been late 8. Sam asked Romeo what ….. with himself the entire Saturday. would he be doing would be he doing he would be doing 9. I knew Linda ….. around Europe for three months already. was travelling had been travelling had travelled 10. Mr. Clemence said that because of the fire part of the building had gone completely, and the rest of it ….. . was falling down had been falling down fell down 11. Len was mistaken when he said that Marion ….. to her new flat the following month. would have moved would be moving moved 12. The personel manager was interested ….. to quit my present job. why had I decided why I had decided why I decided 13. Could you ask Aleks how long ….. at the hotel «Grandston»? would have been staying he would be staying would he be staying 14. Mark replied he didn’t think Jane ….. by the following Sunday yet. would have arrived would arrive had arrived 15. Mary said she was worried that her son ….. very well that year. isn’t studying wasn’t studying hadn’t been studying Усложненные задания: Прочитайте текст и заполните пропуски соответствующими вариантами ответов, представленными в таблице. McDonald’s Dick and Mac McDonald (1)_____ the first McDonald’s in 1948. In San Bernadino, California. In 1954, Ray Kroc also (2) _____ them in their business. By 1959, McDonald (3) _____ its 100 millionth hamburger, and (4) ____ its 100 th store. At that time, McDonald’s (5) _____ at full speed, and Kroc (6) ____ out the McDonald’s began (7) ____ on TV, and in the 1960s added new menu entrees (8) ____ to other countries. The rate that McDonald’s was adding restaurants also (9) ____ steadily. The restaurants (10) by the hundreds each year, and the whole world was able (11) ____ at one. Also, in 1996, McDonald’s (12) ____ restaurants in India, and (13) ____ about in Italy. 1. A. have opened B. opened 2. A. joined B. had joined 3. A. sold B. had been selling 4. A. had opened B. Opened 5. A. went B. had gone 6. A. had bought B. bought 7. A. advertise B. having advertised 8. A. expand B. having expanded 9. A. increased B. was increasing 10. A have opened B. had been opened 11. A. to eat B. eating C. had opened D. Were opening C. has joined D. joining C. Had sold D. have sold C. were opened D. have opened C. has been going D. was going C. was buying D. has bought C. advertising D. advertised C. expanded D. had expanded C. has increased D. increasing C. have been opened D. opened C. to have eaten D having eaten 12. A. has opened B. opened C. had opened D. was opening 13. A. had added B. has added C. added D. was added Microsoft Microsoft is the largest software company in the computer world and its operating systems are on almost all computers. Its release of Windows 95 and the Microsoft Office 95 (1) ____ the size of already giant company. It (2) ____ so successful because of the low priced and easy (3) ____ software it creates. From six year olds to presidents of large corporations use their products. William Gates, a 19-year old dropout from Harvard, (4) ___ Microsoft with his friend Paul Allen. The two (5) ___ BASIC, a language that let people (6) ____ programs for their PC. Then, IBM chose them (7) ____ an operating system for the new IBM-PCs. Gates and Allen (8) ___ $50,000 to Tim Paterson for his QDOS, and (9) ___ it to MS-DOS. The operating system was extremely successful, and soon all other PC manufacturers (10) ___ to be compatible with IBM. This gave Microsoft the chance (11) ___ huge profits, and they (12) ___. Their next big success was Windows, which was a graphical operating system that (13) ___ popular because it was extremely easy to use. Then, in 1993, they (14) ___ Windows NT, which (15) ___ networking extremely easy. By this time, Bill Gates (16) ____ the PC operating system market and (17) ___ a billionaire. 1. A. has increased B. had increased 2. A. is being B. were 3. A. using D. has been using 4. A. found D. had founded 5. A. rewrote C. having increased D. increasing C. has been D. had been C. to use D. has used C. had found D. founded C. had rewritten B. rewrite 6. A. to create B. create 7. A. writing B. to write 8. A. have paid B. paid 9. A. renaming B. had renamed 10. A. wanted B. want 11. A. to make B. making 12. A. did B. was done 13. A. became B. becoming 14. A. releasing B. were released 15. A. making B. had been made 16. A. monopolized B. had monopolized 17. A. became D. are rewriting C. creating D. created C. to have written D. to be writing C. had paid D. paying C. renamed D. having renamed C. had been wanted D. wanting C. having made D. made C. do D. had done C. had become D. to become C. had been released D. released C. made D. to make C. have monopolized D. monopolizing C. had become B. has become D. become Ключи к заданиям: Задание 1. 1. Write; 2. Are … doing; 3. Has … gone; 4. Has not seen. 5. Will go. 6. had… told; 7. Does not work; 8. Will… switch off; 9. Was writing; 10. Does not like. Задание 2. 1. is looking. 2. are playing; 3. Is listening; 4. Are watching; 5. Is working; 6. Are asking; 7. Is translating; 8. Are doing. Задание 3. 1.came, had started; 2. Went; 3. Was leaving; 4. Has… understood; was travelling; 5. Spoke; 6. Was… played; 7. Was going; 8. Played; 9. Were discussing; 10. Was raining. Задание 4. 1. A; 2. B; 3. A; 4. C; 5. A; 6. A Задание 5. Тест по теме «Present Tenses» 1. Want; 2. Has arrived; 3. Has not heard; 4. Attend; 5. Contains; 6. Are telling; 7. Hasn’t read; 8. Know; 9. Increases; 10. Jogs; 11. Has been moving; 12. Hasn’t played. 13. Am waiting; 14. Have you done; 15. Haven’t seen. Тест по теме “Past Tenses” 1. Had rained; 2. I was looking; 3. Lived; 4. Told; 5. Had blown; 6. Had made; 7. Was waiting; 8. Had crashed; 9. Hadn’t looked; 10. Were walking; 11. Had described; 12. Had been watching; 13. Had broken; 14. Had fought; 15. Hit. Тест по теме «Future Tenses» 1. Starts; 2. Will have made up his mind; 3. Will take part; 4. Will show; 5. Am going to do; 6. Won’t have left; 7. You will still be working; 8. Will find; 9. Will come; 10. Will have been working; 11. Will have finished; 12. Will have found; 13. Will come; 14. Meet; 15. Will be dining. Тест по теме “Sequences of Tenses” 1. Would wait; 2. Hadn’t known; 3. Paid; 4. Not to buy; 5. Was closed; 6. He might use. 7. Had never been late; 8. Would he be doing; 9. Had been travelling; 10. Was falling down; 11. Would be moving; 12. Why I had decided; 13. Would he be staying; 14. Would have arrived; 15. Wasn’t studying. Список использованной литературы: 1.Агабекян И.П. Английский язык для ССУЗОВ: учебник. – М.: ООО «Издательство Проспект», 2007. – 228 с. 1. Агабекян И.П., Коваленко П.И. Английский для инженеров: учебник. Высшее образование. Ростов-на-Дону «Феникс», 2004.-318с. 2. Бонк Н.А. Английский шаг за шагом: Курс для начинающих. – М.: ЗАО «РОСМЭН — ПРЕСС», 2009. – 523 с. 3. Шевелева С.А. English on Economics: учебн. пособие для студентов вузов. – М.: ЮНИТИ – ДАНА, 2009. – 456 с. 4. Голубев А.П., Н.В. Балюк., И.Б. Смирнова Английский язык: учебное пособие для студ. Сред. Проф. Учеб. Заведений. – М.: Издательский центр «Академия», 2010. – 333 с. 5. Качалова К.Н., Израилевич Е.Е. Практическая грамматика английского языка. – СПб.: БАЗИС, КАРО, 2008. – 608 с. 6. Клементьева Т.Б. Счастливый английский: Сборник упражнений. – М.: «Дрофа», 1998. – 288 с. 7. Клементьева Т.Б., Шэннон Д.А. Счастливый английский. Кн.2 для 79кл. общеобразов. шк. – 2-е изд., испр.- Обнинск: Титул, 1999. – 448 с. 8. Кузовлев В.П. Английский язык // Учебник для 5 классов. – М.: Просвещение, 1998. – 211 с. Дополнительные источники: Интернет ресурсы: http: // image.websid.ru http: // studentbank.ru