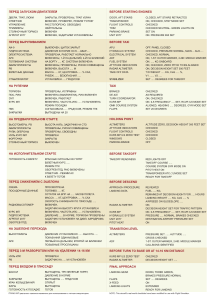
1. ACC (Area Control Centers) = Controls are usually located in the vicinity of the airports. 2. The airspace consists / is made up of controlled and uncontrolled airspaces. 3. On the airways a pilot must accomplish Air traffic Controller’s instructions (along the airways). 4. A Prohibited area is an area where flights are prohibited / forbidden. 5. Who will be imposed responsibility for any incidents in the open airspace on? Who will be responsible / take responsibility for … 6. Within one FIR (Flight Information Region) different / various flying vehicles such as planes, gliders, hot air balloons, helicopters can fly. 7. Why is it necessary to regulate airspace? Why must airspace be regulated? 8. In controlled airspace ATC is provided to all flights. 9. Advisory Routes are allocated Class “F”. 10. The flight plan was filed / given by the captain on time. 11. Flight Information Region (FIR) takes its name from names of big cities. The name of FIR is taken from names of major cities. 12. What maintenance are aircraft provided with on / along advisory routes? 13. A Control Zone (CTR) is controlled airspace which extends from the ground level up to a specified (certain) flight level (FL) or altitude. 14. In visual flight a pilot is responsible for safe separation. 15. The ATC controller gave clearance (permission) to change (switch from) VFR (Visual Flight Rules) to IFR (Instrument Flight Rules) due to low visibility. 16. Each airway has its own identification code. 17. What’s the main difference between VMC (Visual Meteorological Conditions) and IMC (Instrument Meteo Conditions)? 18. Terminal Control Areas (TMA) are located in the vicinity of large aerodromes. 19. A danger area is an area where flights can be hazardous / dangerous. 20. An air traffic controller can cancel a flight plan if an aircraft changes Instrument Flight Rules to Visual Flight Rules.