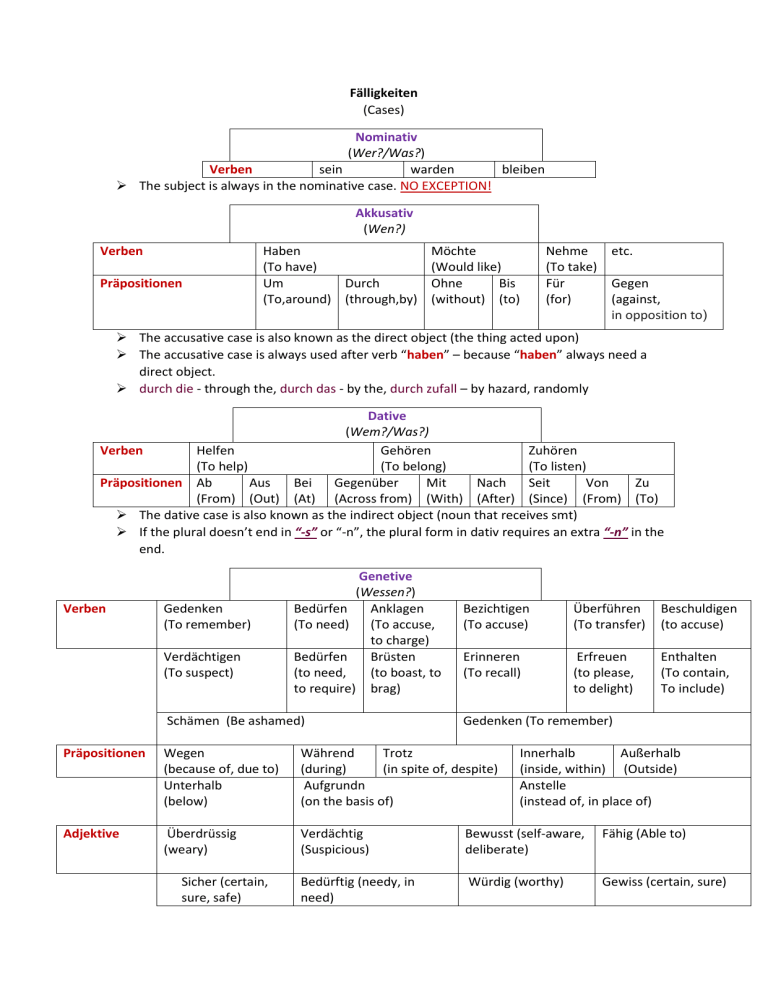
Fälligkeiten (Cases) Nominativ (Wer?/Was?) Verben sein warden bleiben The subject is always in the nominative case. NO EXCEPTION! Akkusativ (Wen?) Verben Präpositionen Haben (To have) Um Durch (To,around) (through,by) Möchte (Would like) Ohne Bis (without) (to) Nehme (To take) Für (for) etc. Gegen (against, in opposition to) The accusative case is also known as the direct object (the thing acted upon) The accusative case is always used after verb “haben” – because “haben” always need a direct object. durch die - through the, durch das - by the, durch zufall – by hazard, randomly Dative (Wem?/Was?) Verben Helfen Gehören Zuhören (To help) (To belong) (To listen) Präpositionen Ab Aus Bei Gegenüber Mit Nach Seit Von Zu (From) (Out) (At) (Across from) (With) (After) (Since) (From) (To) The dative case is also known as the indirect object (noun that receives smt) If the plural doesn’t end in “-s” or “-n”, the plural form in dativ requires an extra “-n” in the end. Verben Gedenken (To remember) Verdächtigen (To suspect) Genetive (Wessen?) Bedürfen Anklagen (To need) (To accuse, to charge) Bedürfen Brüsten (to need, (to boast, to to require) brag) Schämen (Be ashamed) Bezichtigen (To accuse) Überführen (To transfer) Beschuldigen (to accuse) Erinneren (To recall) Erfreuen (to please, to delight) Enthalten (To contain, To include) Gedenken (To remember) Präpositionen Wegen (because of, due to) Unterhalb (below) Während Trotz (during) (in spite of, despite) Aufgrundn (on the basis of) Adjektive Überdrüssig (weary) Verdächtig (Suspicious) Bewusst (self-aware, deliberate) Fähig (Able to) Bedürftig (needy, in need) Würdig (worthy) Gewiss (certain, sure) Sicher (certain, sure, safe) Innerhalb Außerhalb (inside, within) (Outside) Anstelle (instead of, in place of) The genitive case signals belonging or possession. M and N require an extra “-s” or “-es” Nouns that ends in “-s”, “-ß“, „-x“, „-z“ „-ES“ must be used.